In-depth Understanding of Client-side script on Model Driven and Dynamics 365
In this Power Platform article, we’ll look at how to add client-side scripting to a Model Driven App. Read on to learn how to use a client-side script in Model-driven or Dynamics 365 Forms, as well as what methods and collections are available. I’ll attempt to answer as many questions as possible in order to gain a thorough understanding of the implementation of client-side script on model-driven apps and Dynamics 365.
This blog post would be 4 parts of a series.
1st blog, this dedicated to basic's client-side scripts on web resources, event handlers, execution context, and formContext.
2nd blog is dedicated to Data Object, which focuses on how to interact and retrieved entity/table and Column values.
3rd blog is dedicated to UI Object, which focuses on UI elements of Model-driven apps such as Forms, Tabs, and sections.
4th blog is dedicated to XRM.API, which focuses on database/dynamics 365 rest API operation on Model Driven form with client-side script Web resources.
Now flow along with me for step-by-step instructions:
What is Client-side scripting on Model Driven App?
The client-side allows us to use JavaScript on the model-driven app to implement custom business logic. This should be used as an alternative if standard model-driven app business rules do not meet the requirements. Client-side scripting will help to implement custom business logic.
Client-Side scripts run on model-driven apps with response to form-level events, such as:
- Form Load event
- Data change event
- Form Save event
- Command bar, invoke the client-side script on button click event
Now, we will be looking at what are the common tasks that can be done using client-side scripting on Form.
- Get or Set values of a Form attributes
- Show and Hide user Interfaces such as Tabs, sections, and attributes
- Model-driven form switching, if have multiple forms
- Open dialog box, forms, reports, and custom web resources (HTML pages)
- Interact with Business process flow
The high-level structure of Client-side scripting API object model and namespaces
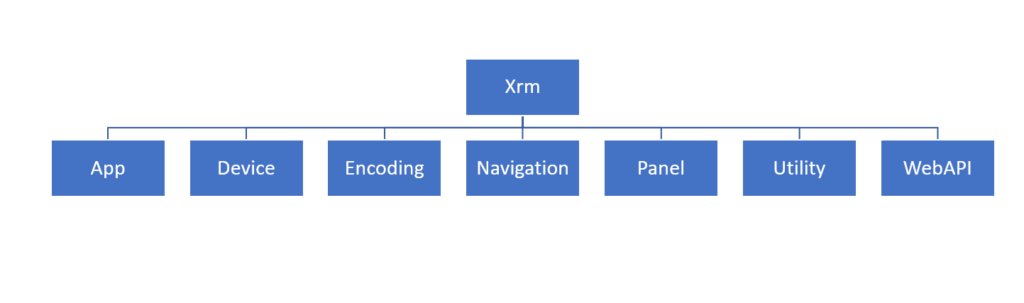
App: Provides App-related methods such as event handlers for any app-level notifications.
Device: Provides methods to use native device capabilities such as image, video, audio, location, and more.
Encoding: Provides methods to encode and decode scripts (useful for HTML and XML).
Navigation: Provides navigation-related methods, such as opening the Alert or Confirm dialog box, opening File, URL, and more.
Panel: Provides a method to open a web page on the side panel of model-driven form.
Utility: Provides information about entity/table metadata, table status transition, current origination setting, and many more.
Web API: Provides properties and methods to use Web API.
What are Event Handlers?
Client Script logic runs as an event handler for the form events. Here we must register events on the form to have your logic to executed and some events can be executed from code.
How to register Client script on Model-driven form with help of Event Handlers
In the Form designer you can register event handlers for the following events:
Form: It allows you to register the event on Form “OnLoad” and “OnSave” Event handlers
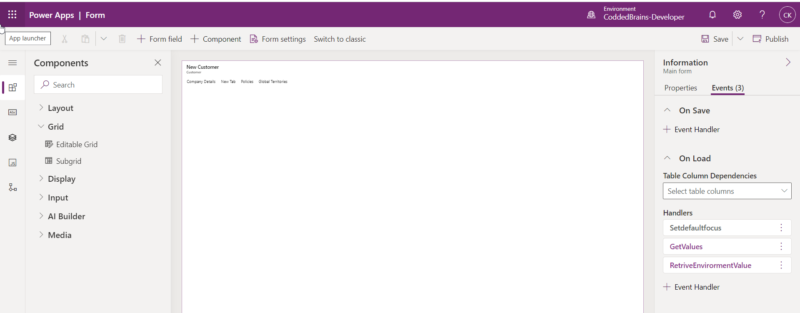
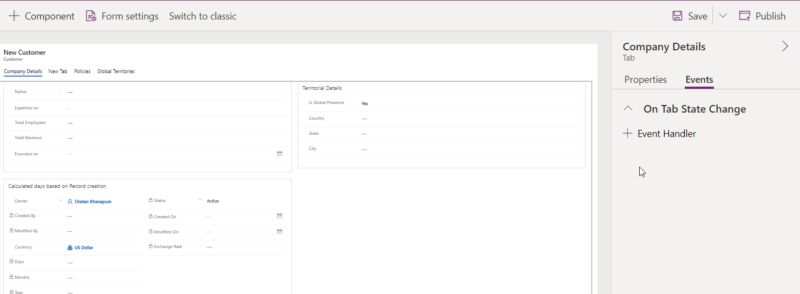
Tabs: Allows you to register the event on the “On Tab State Change” event
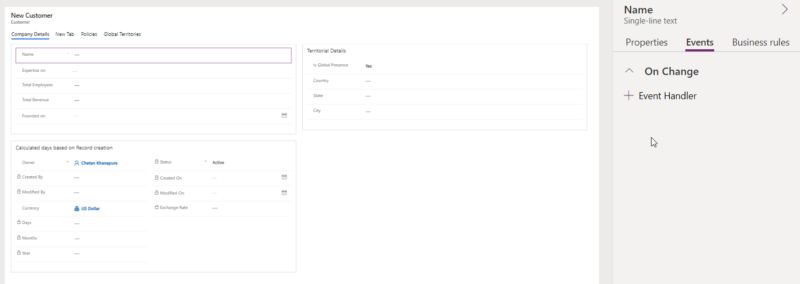
Columns: Allows you to register event on “On Change”
How to register client script on Event Handler
Go to Form, then Events, and then chose Event Type as “On Load” and then select the JavaScript library from the dropdown option where the code was written, followed by the function name, with both “Enable” and “Pass Execution context as first parameter” marked as checked.
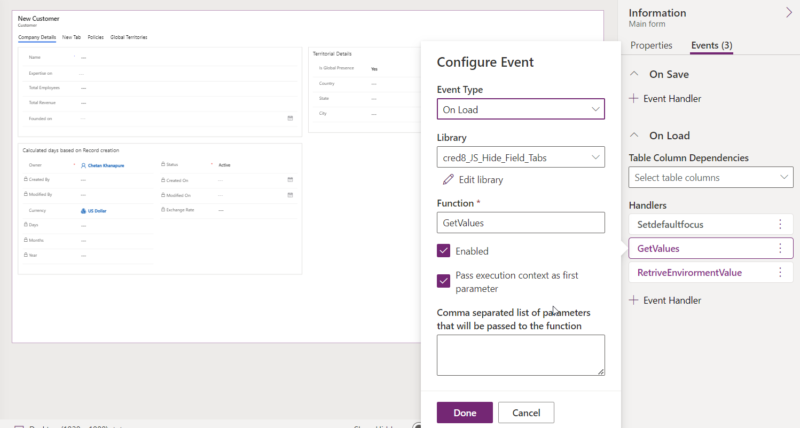
What is the Execution context?
When you register the event handler, you can pass execution context as the first parameter, on the above pic you can see the checkbox is checked here, The importance of execution context is it will retrieve the model-driven Form and Grid context. Now let's see the declaration in JavaScript code:
What exactly is Form context?
It is a Client API form context (formContext), and by creating an object, it will provide a reference to the form, such as getting the values of the columns on the form or hiding or showing a tab, section, or any columns of a form or retrieving a row from a grid.
High-level overview of formContext Diagram
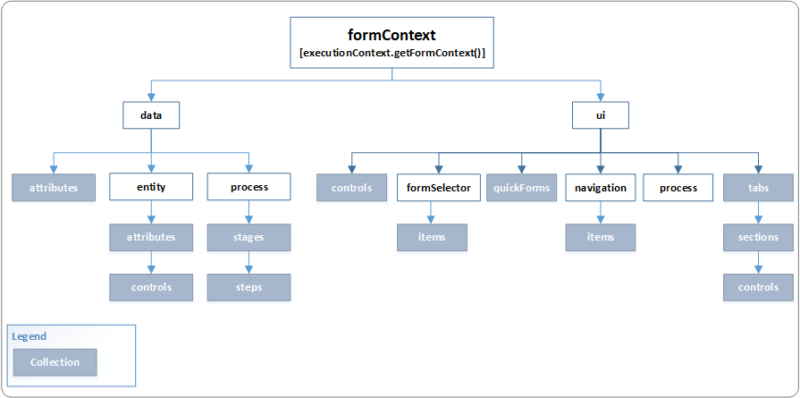
Here will see both the Data object & UI object in detail along with code snippet examples:
Data Object (formContext.data)
It is very useful to retrieve or perform any action on the Table/entity level such as retrieving column values, it has been categorized into three sections.
- Attributes – It helps to retrieve the column value containing data in the model-driven app form or grid
Ex: formContext.data.entity.attributes
- Entity – It helps to retrieve the information that is specific to the row that is displayed on Form, here you can perform the Save operation
Ex: formContext.data.entity.addOnSave(myFunction)
- Process- It provides the method, events, and objects to interact with Business process flow on a form. The given example below will help to add a JavaScript function as an event handler for stage change, so that a custom JavaScript event is called when a business process stage change event is called
Ex: formContext.data.process.addOnStageSelected(myFunction)
UI object (formContext.ui)
The UI Object is providing the methods to retrieve information of user interfaces such as Tabs, sections, business process flow, and collection of several other components of form and grid.
- Controls – It represents an HTML element that is present on a Model-driven form, Control object will provide the method to change the presentation and behavior of controls
Ex: formContext.ui.controls
formContext.ui Section.controls
- FormSelector – It provides a method to retrieve information about the form that is currently in use. Use the formSelector.items collection to return information about all the forms that are available for the user, below example will use to retrieve the form name.
Ex: formItem = formContext.ui.formSelector.getCurrentItem();
formItem.getLabel();
- Navigation- It provides the collection of all the navigation items on the page.
(Note: This method would not work on Dynamics 365 Tablet mode)
- Process – Provides objects and methods to interact with the business process flow control on a form, such as a hide or show.
- QuickForms- It provides the collection of all quick view controls of the model-driven app.
Ex- quick view control = formContext.ui.quickForms.get(arg)
- Tabs – It provides the collection of all tabs on the form.
Ex- var tabObj = formContext.ui.tabs.get(arg);
Conclusion
Client-side scripting is very important when you have complex validation rules to implement on a form, grid, or even a business process flow. We can also enhance the UI elements to meet the needs of the business.
Comments
Post a Comment